The Use of Tetrahedral Framework Nucleic Acids in Pancreatitis Treatment Drugs
2024-06-26
Background:
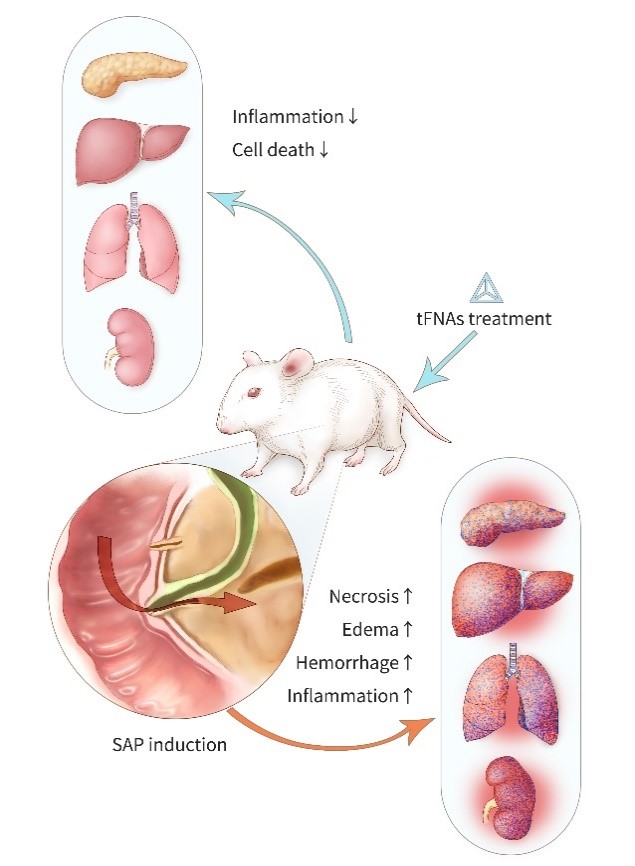
Severe Acute Pancreatitis (SAP) is an inflammatory disease of the pancreas characterized by severe damage and necrosis of pancreatic tissue. It not only affects the pancreas but also triggers a systemic inflammatory response, leading to multi-organ failure and potentially death. Currently, there is no effective treatment to reverse the progression of SAP. In related research for this patent, tetrahedral framework nucleic acids (tFNAs) have been used to treat SAP and have been shown to have significant effects in suppressing inflammation and preventing cellular pathological death. After tFNA treatment, significant changes were observed in serum biomarkers related to SAP in mice: the levels of several important cytokines involved in both local and systemic inflammatory responses were significantly downregulated, and the expression levels of proteins related to cellular necrosis and apoptosis were also notably altered. Overall, our experimental results indicate that tFNAs treatment can be used to treat SAP and its associated multi-organ damage in mice, providing a potential new and effective therapeutic approach for SAP.
Cutting-Edge Research Findings:
Tetrahedral framework nucleic acids (tFNA), also known as tetrahedral DNA or tetrahedral DNA nanostructures, are a novel type of nanoparticle with specific sequences, dimensions, and conformations. tFNAs are formed by the self-assembly of four single-stranded DNAs into a three-dimensional tetrahedral structure. They have the ability to regulate various cellular biological behaviors, including proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and autophagy. tFNAs have also demonstrated strong anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties. Preliminary studies show that tFNAs can effectively suppress both local and systemic inflammatory responses, reduce apoptosis, and mitigate tissue damage caused by inflammation in various inflammatory diseases such as acute kidney injury and periodontitis.
Based on this research, we decided to investigate the use of tFNA for treating SAP and its effects on the pancreas and related organs. We found that tFNA can reduce the expression of inflammatory factors in blood and tissues, modulate the expression of specific apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins, and reduce cellular apoptosis, thereby alleviating tissue damage in the pancreas and multiple organs. Our findings propose a new method for treating SAP and its associated multi-organ damage and demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of this approach in animal models.
Research Methods:
AFM, TEM, and PAGE were used to characterize the synthesis of tFNA.
Small animal in vivo imaging was used to detect the distribution and stability of tFNA in multiple organs of mice.
ELISA was employed to measure the levels of inflammatory factors in blood and tissues.
TUNEL staining was used to assess cellular apoptosis in tissues.
Immunofluorescence staining was used to detect the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins.
Animal experiments were conducted to evaluate the therapeutic effects of tFNA on SAP.
Experimental Results:
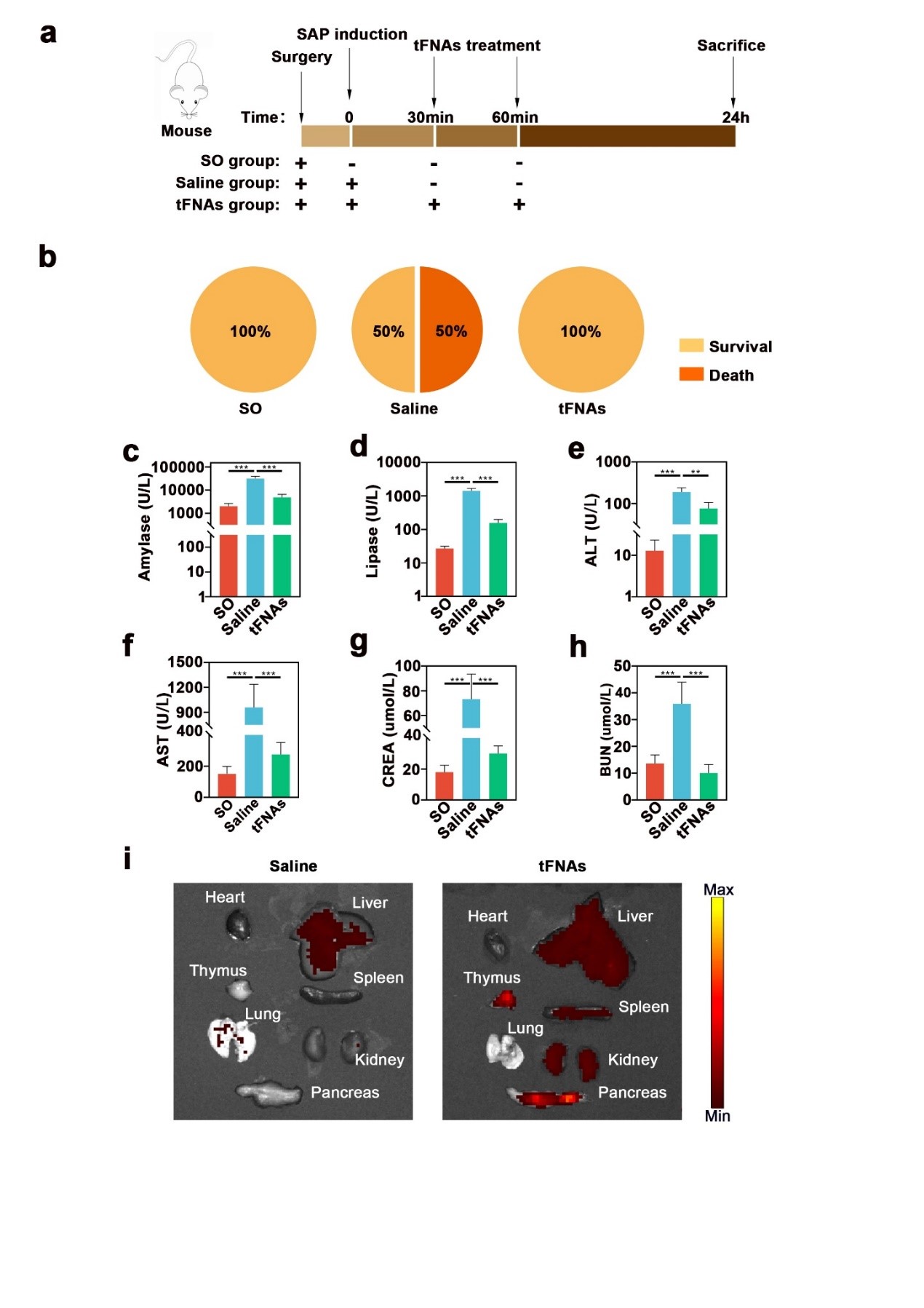
The research team successfully synthesized tetrahedral framework nucleic acids (tFNA). In the SAP mouse model, tFNA exhibited excellent anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic capabilities. Compared to the control group, tFNA significantly reduced the mortality rate in SAP mice. Biochemical indicators in the blood showed that tFNA could protect the normal functions of the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and lungs. ELISA results demonstrated a significant decrease in the levels of inflammatory factors in blood and tissues. Histological results showed that tFNA could reduce tissue structural damage and apoptosis in the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and lungs caused by SAP. Immunofluorescence staining results indicated that tFNA inhibited the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins Caspase9 and Bax, and promoted the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, thereby reducing cellular apoptosis.
Research Conclusion:
Our study shows that tFNA treatment effectively alleviates SAP and its associated multi-organ damage in mouse models. tFNA treatment can reduce the levels of inflammatory factors in blood and tissues, suppress local and systemic inflammation, and regulate the expression of apoptosis-related proteins to reduce cellular apoptosis. This protects the normal tissue structure and function of the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and lungs. Our research may provide a new treatment option for patients with severe acute pancreatitis in the future.
Published Paper:
Nano Letters 2022, 22(4), 1759-1768, IF=12 DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c05003